Advertisement
Working with data in Excel often feels like organizing a crowded room. Some things are numbers you need to calculate, while others are just notes or labels sitting around. That’s where COUNT and COUNTA in Excel come into play — like two reliable tools in a messy toolbox. One focuses only on numbers, while the other counts anything that’s not empty.
They might sound basic, but these functions are the quiet problem-solvers behind clean reports and accurate data analysis. Before diving into complex formulas, learning to use COUNT and COUNTA in Excel is like mastering the basics of keeping your workspace in order.
When it comes to numbers in Excel, the COUNT function is your go-to tool for keeping track of them. Its job is straightforward — it counts how many cells in a selected range actually contain numeric values. It doesn’t get distracted by text, empty cells, or error messages. That singular focus makes it incredibly useful when dealing with large sets of numerical data.
Imagine you're tracking monthly revenue in a spreadsheet. Some cells may be empty; others might have comments or text labels. Using the COUNT function lets you ignore all that noise and zero in on just the cells with real numbers.
The basic syntax is clean and simple: =COUNT(range)
For instance, if you're working with A1 to A10 and want to know how many of those cells contain numbers, =COUNT(A1:A10) gives you the exact count. If two of those cells have text and one is blank, COUNT still gives you a precise result by ignoring anything that’s not a number.
It’s especially handy when reviewing shared files or imported data where entries can get messy. COUNT lets you confirm the actual quantity of numeric inputs at a glance, which is crucial for accurate averages and totals and for spotting missing values. It's a small function with a big impact on clarity and confidence in your data.
While COUNT is strictly focused on numbers, COUNTA in Excel casts a wider net. It counts every non-empty cell in a selected range, whether it holds numbers, text, symbols, or even errors. The only thing it skips is empty cells. This makes it an incredibly useful tool when you're working with varied or mixed data types.
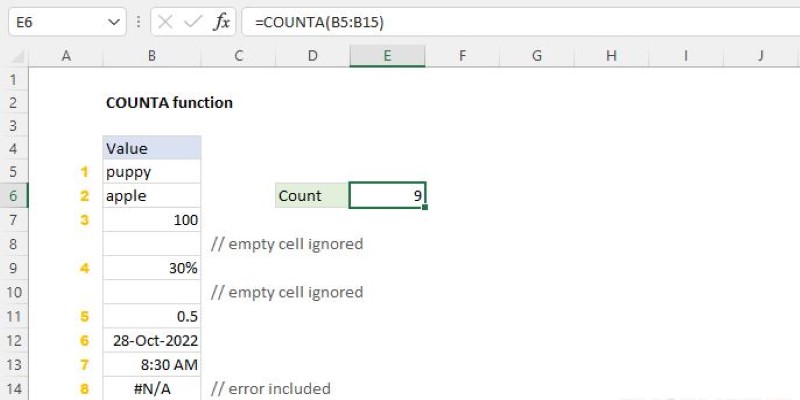
Let’s say you’re managing a customer feedback log, an employee tracker, or a product inventory list. These kinds of spreadsheets often contain a mix of names, dates, product codes, or notes. Using COUNTA gives you a quick count of how many entries exist — without worrying about whether those cells hold numbers or text.
Its syntax is simple: =COUNTA(range)
If you use =COUNTA(A1:A20), Excel will return the number of non-blank cells in that range. It doesn’t matter if those cells hold text, numbers, or even errors — COUNTA will count them all.
This function shines in shared workbooks and collaborative settings. Instead of manually checking each cell, COUNTA helps you spot missing data, track form submissions, and stay on top of progress. It’s a small formula with big utility, especially when consistency and completeness matter.
Understanding the difference between COUNT and COUNTA in Excel is crucial because using the wrong function can lead to incorrect results.
The primary difference is simple: COUNT counts only numeric values, while COUNTA counts all non-empty cells regardless of content.
Consider a list in Excel where some cells contain numbers, some contain text, and others are blank. If you apply both functions to the same range, you’ll get different results.
For example, if range A1:A5 contains:
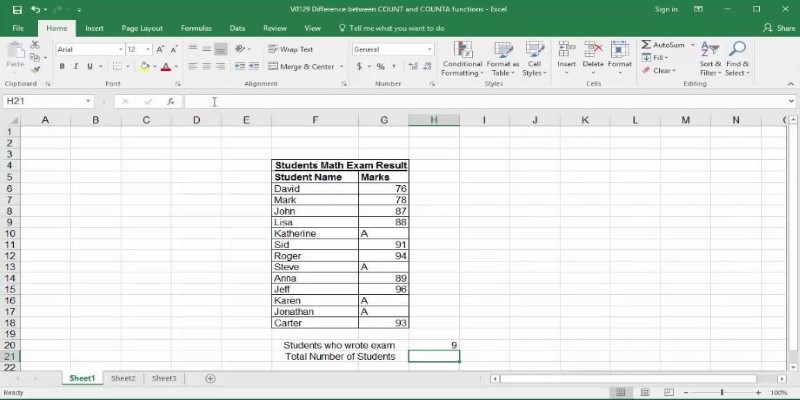
Using =COUNT(A1:A5) will return 2 because only two cells (A1 and A3) have numbers.
Using =COUNTA(A1:A5) will return 4 because four cells (A1, A2, A3, A5) are not empty.
This distinction is essential when analyzing datasets. If your goal is to count only numeric entries, COUNT is the correct function. If you’re more interested in counting all filled cells regardless of content, COUNTA is the better choice.
These differences also highlight the importance of understanding your data before applying functions. Misusing COUNT when you actually need COUNTA (or vice versa) can lead to reporting errors, misinterpretation of data, and poor decision-making.
Moreover, knowing the difference between COUNT and COUNTA in Excel makes your formulas clearer to others. When sharing spreadsheets in a team setting, clear function use signals your intent to readers and collaborators.
COUNT and COUNTA in Excel often serve as the building blocks of larger, more complex reports. They help simplify tasks that might otherwise require unnecessary workarounds. In sales reports, COUNT ensures averages and totals are based only on actual numeric data. This prevents skewed results when cells are empty or hold irrelevant content.
In project management or tracking sheets, COUNTA is especially useful for monitoring inputs like status updates, progress notes, or task completions. It gives a quick count of all filled entries, helping users see what’s been submitted and what’s missing.
These functions are also critical in dashboards. Behind-the-scenes formulas often rely on COUNT or COUNTA to update summary visuals. They also play a key role in data validation and highlight issues when expected data is missing — especially when used with conditional formatting.
When combined with other functions like IF, AVERAGE, or VLOOKUP, they create dynamic systems. For best results, label formulas clearly so others can follow your logic easily in shared spreadsheets.
COUNT and COUNTA in Excel may seem simple, but their role in data management is essential. They help users bring clarity to their spreadsheets, ensuring accurate counts of numbers or non-empty cells. Whether you're handling sales data, customer lists, or project records, these functions provide quick, reliable answers. Understanding the difference between COUNT and COUNTA in Excel allows you to work smarter, avoid errors, and keep your data organized. In the world of Excel, mastering these basics sets the foundation for everything else.
Advertisement

Understand the Difference Between Non Relational Database and Relational Database through clear comparisons of structure, performance, and scalability. Find out which is better for your data needs
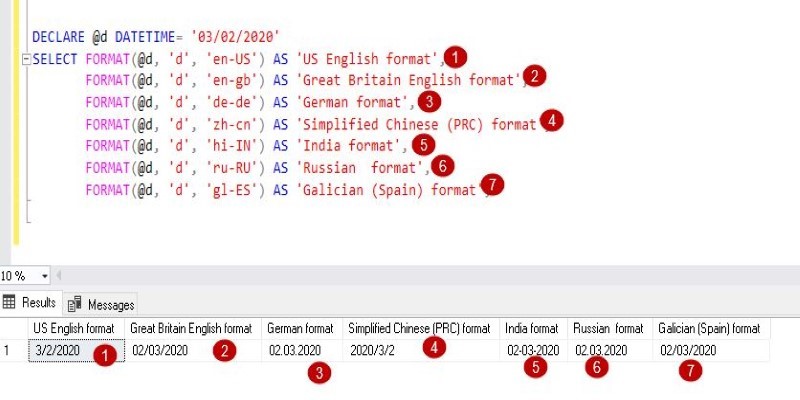
The FORMAT() function in SQL transforms how your data appears without changing its values. Learn how to use FORMAT() in SQL for clean, readable, and localized outputs in queries

Discover DuckDB, a lightweight SQL database designed for fast analytics. Learn how DuckDB simplifies embedded analytics, works with modern data formats, and delivers high performance without complex setup
Confused between Data Science vs. Computer Science? Discover the real differences, skills required, and career opportunities in both fields with this comprehensive guide

Building smart AI agents with LangChain enables developers to create intelligent agents that remember, reason, and act across multiple tools. Learn how the LangChain framework powers advanced prompt chaining for real-world AI automation

Few-Shot Prompting is a smart method in Language Model Prompting that guides AI using a handful of examples. Learn how this technique boosts performance and precision in AI tasks
How the AI Robotics Accelerator Program is helping universities advance robotics research with funding, mentorship, and cutting-edge tools for students and faculty

Volkswagen introduces its AI-powered self-driving technology, taking full control of development and redefining autonomous vehicle technology for safer, smarter mobility

Stay updated with AV Bytes as it captures AI industry shifts and technological breakthroughs shaping the future. Explore how innovation, real-world impact, and human-centered AI are changing the world

Gain control over who can access and modify your data by understanding Grant and Revoke in SQL. This guide simplifies managing database user permissions for secure and structured access

Gemma Scope is Google’s groundbreaking microscope for peering into AI’s thought process, helping decode complex models with unprecedented transparency and insight for developers and researchers

How the ElevenLabs API powers voice synthesis, cloning, and real-time conversion for developers and creators. Discover practical applications, features, and ethical insights