Advertisement
Working with data often feels heavier than it needs to be. Many database systems demand servers, complex configurations, and more resources than the task really calls for. DuckDB offers a refreshing alternative — a small, embedded analytics engine designed for speed and simplicity. It runs directly inside your application, handles analytical workloads with ease, and works well with the tools and formats you already use. Whether you’re crunching numbers in Python, querying local files, or building a reporting feature into software, DuckDB helps you get answers fast without getting bogged down in infrastructure. Here’s what makes it stand out.
DuckDB is a lightweight, columnar SQL database engine designed specifically for analytics. Often described as the “SQLite of analytics,” it follows a similar philosophy — embedding directly into your application so you don’t have to run a separate server. Where SQLite shines at transactional workloads, DuckDB is tuned for analytical tasks. Its columnar storage format lets it sift through and process large datasets efficiently, making operations like aggregations, filters, and joins much faster than traditional row-based databases.
Since DuckDB runs in-process, it works right alongside your code, sharing the same memory space. Whether you’re writing in Python, R, or C++, you can load data from CSV or Parquet files, run SQL queries, and keep everything local. This eliminates network delays and the usual headaches of configuring a server. Its support for standard SQL makes it easy to pick up, and its tight integration with tools like Pandas and Apache Arrow bridges the gap between databases and modern data analysis workflows.
Open source, portable, and incredibly easy to set up, DuckDB works anywhere — scripts, desktop applications, even web services — offering high performance without unnecessary complexity.
DuckDB fills a gap in the database landscape: efficient analytics at a small scale without the complexity of distributed systems. Many OLAP systems assume clusters and large budgets, but DuckDB assumes your data fits on a single machine and uses local resources effectively.
Its performance is a major advantage. Columnar storage and vectorized execution allow it to process millions of rows quickly. Analytical queries — especially those scanning, joining, and aggregating — are much faster compared to row-based databases because only the relevant columns are read.
Simplicity is another strength. There’s no server to set up, no separate accounts to manage, no background process to monitor. You just include the library, open a connection to a file or in-memory database, and start running queries. This is especially useful for embedding analytics into applications or workflows where external servers would complicate things.
DuckDB is also well-suited to modern data formats. It can read Parquet and Arrow files directly, which is common in big data and analytics, so you can query large files without loading them into a traditional database. Integration with Python and R is smooth, letting you combine the familiar flexibility of DataFrames with the power of a SQL engine.
Being transactional and ACID-compliant adds reliability, which is rare in lightweight analytics tools. This ensures consistent results even with concurrent operations or errors.
DuckDB’s design makes it useful in many real-world situations. One common use is interactive exploration of local datasets. Analysts often work with data that is too large for spreadsheets but not large enough to justify a data warehouse. DuckDB is perfect here — you can query gigabytes of Parquet or CSV files directly and get quick results.

It also serves well as a backend for applications that need analytics features. For example, a desktop reporting tool can use DuckDB to calculate summaries, generate tables, or build charts without depending on an external server. It's an in-process design, and local storage keeps the setup simple and the performance solid.
For data science, DuckDB can replace heavier tools for working with structured data. Large datasets often push Pandas to its limits, but DuckDB handles them more efficiently while still letting you work with familiar DataFrames. You can run SQL queries on Parquet or Arrow files, then convert results into DataFrames if needed.
DuckDB’s direct support for Parquet and Arrow files simplifies working with cloud storage as well. Many pipelines already output data in these formats, and DuckDB can query them directly without requiring ETL steps.
Its transaction support and predictable performance make it reliable even when multiple queries run at once. This combination of speed, simplicity, and modern format support makes it versatile across industries and workflows.
DuckDB reflects a growing shift in how people handle data. More applications need to process structured data quickly and locally, without relying on remote servers. Embedded analytics is becoming more common, and DuckDB fits this model by offering SQL-based analytics in a compact, easy-to-use package.
The project is under active development with an engaged open-source community. Improvements such as better parallel processing, richer SQL support, and smarter memory use are ongoing. Its expanding integrations with tools and data formats make it even more flexible for a wide range of tasks.
Getting started with DuckDB is straightforward. You install it in seconds, and it works with your existing data formats and tools. Whether you’re analyzing local files, building an app with reporting features, or working on structured datasets that don’t need a full server-based solution, DuckDB is a practical choice for embedded analytics.
DuckDB stands out for making analytics simple, fast, and accessible. By combining the convenience of an embedded system with the efficiency of a columnar analytical engine, it meets the needs of those working with structured data without adding unnecessary complexity. It supports familiar formats, integrates with common tools, and performs well even with large datasets on a single machine. For anyone looking to bring SQL-based analytics into applications or workflows in a lightweight, reliable way, DuckDB offers a sensible and effective solution.
Advertisement

Gemma Scope is Google’s groundbreaking microscope for peering into AI’s thought process, helping decode complex models with unprecedented transparency and insight for developers and researchers
Understand how TCL Commands in SQL—COMMIT, ROLLBACK, and SAVEPOINT—offer full control over transactions and protect your data with reliable SQL transaction control

Gain control over who can access and modify your data by understanding Grant and Revoke in SQL. This guide simplifies managing database user permissions for secure and structured access
How the SUMPRODUCT function in Excel can simplify your data calculations. This detailed guide explains its uses, structure, and practical benefits for smarter spreadsheet management
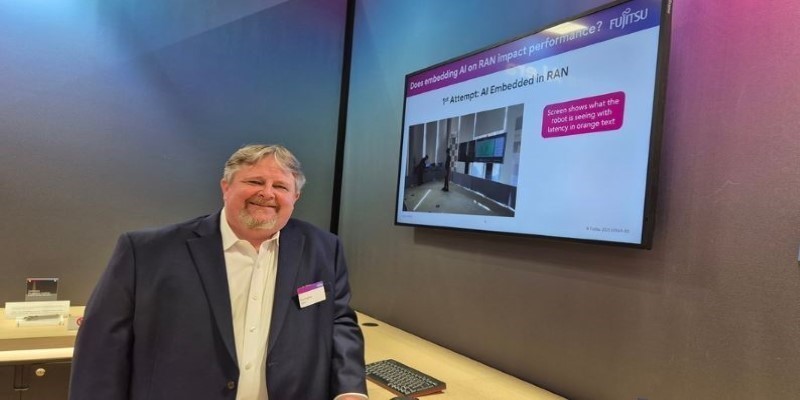

Fujitsu AI-powered biometrics revealed at Mobile World Congress 2025 claims to predict crime before it happens, combining real-time behavioral data with AI. Learn how it works, where it’s tested, and the privacy concerns it raises

Learn how process industries can catch up in AI using clear steps focused on data, skills, pilot projects, and smart integration
Understand what Python Caching is and how it helps improve performance in Python applications. Learn efficient techniques to avoid redundant computation and make your code run faster

Find out the Top 6 Humanoid Robots in 2025 that are transforming industries and redefining human-machine interaction. Discover how these advanced AI-powered robots are shaping the future of automation, customer service, and healthcare

How the Chain of Verification enhances prompt engineering for unparalleled accuracy. Discover how structured prompt validation minimizes AI errors and boosts response reliability
How the AI Robotics Accelerator Program is helping universities advance robotics research with funding, mentorship, and cutting-edge tools for students and faculty

Google AI open-sourced GPipe, a neural network training library for scalable machine learning and efficient model parallelism

Understand the Difference Between Non Relational Database and Relational Database through clear comparisons of structure, performance, and scalability. Find out which is better for your data needs