Advertisement
Germany has officially opened an AI self-driving test hub, and it's not just another proving ground with cameras and cones. It's a government-backed facility designed to test real-world scenarios at scale, including urban traffic, rural roads, and even unpredictable human behavior. Instead of just running prototype vehicles in isolated conditions, this hub replicates the friction of daily life: kids darting into the street, confusing signage, sudden weather changes, and road repairs. For a country that already leads in automotive innovation, this isn't just another project. It's a public statement about where autonomous driving is actually headed—out of labs and into the messy reality of everyday life.
The facility, located in North Rhine-Westphalia, is part of a broader European initiative to integrate AI into transport infrastructure. But unlike closed circuits or simulation-based centers, this test hub blends artificial intelligence directly into live testing environments. Vehicles running through the site are expected to interact with smart traffic lights, sensor-equipped crosswalks, and 5G-connected pedestrian zones. The site was co-developed by a mix of German automotive firms, AI startups, and local authorities, with support from the federal government.
The main keyword for this facility is integration. Vehicles won’t be tested in isolation—they’ll be judged on how well they respond to human-driven cars, cyclists, animals, unpredictable weather, and sudden detours. Think of it as a stress test for AI mobility, highlighting its weak points. And there are many. Current autonomous driving software tends to falter with erratic pedestrian behavior, heavy rain, and non-standard road layouts—challenges that this new center is built to simulate. It's not about making a car that just follows rules, but one that adapts to reality.
In terms of size, the hub spans several kilometers and features mock towns, highway stretches, and even construction zones with movable obstacles. There are areas rigged to simulate night-time driving with minimal lighting, while others feature curved country roads with poor GPS reception—another weak spot for many current systems. The goal is straightforward: to empower AI to handle tasks that humans already deal with every day. If it can't, it's not ready.
Germany's move isn't happening in a vacuum. The country's automotive industry is under pressure. With global players like Tesla rolling out self-driving features and China pushing ahead with connected vehicle corridors, German manufacturers face a clear choice: adapt quickly or fall behind. The AI self-driving test hub is part of a strategy aimed at closing the readiness gap. Testing in simulated conditions is no longer sufficient. Regulators want proof that these vehicles can coexist with the chaos of the real world.
Another reason is regulation. Germany passed a law in 2021 that allows Level 4 autonomous vehicles (those that don't require human attention in certain settings) to operate on public roads under specific conditions. However, implementation has lagged, primarily because there haven't been sufficient controlled environments to test safety parameters. This new hub fixes that. It offers a setting where AI mobility companies can fine-tune their software while meeting legal requirements.
The hub also provides German authorities with a location to collect data. Not just about how AI behaves, but how it fails. That data will help shape not just product development but also legislation. Rather than waiting for incidents on public roads, the idea is to study failure in a controlled but realistic environment. The AI self-driving test hub serves as both a laboratory and a courtroom, providing evidence to inform decisions on whether to accelerate or slow down deployments based on its findings.
The implications go beyond Germany. If this model proves successful, it could serve as a template for AI mobility centers across Europe. The EU has struggled to create a shared testing standard for autonomous vehicles. Different countries administer different tests, with little consistency in the requirements. Germany's hub, with its hybrid of city and country settings, offers something closer to a pan-European benchmark.

It also shifts how AI in vehicles is judged. Instead of emphasizing lab-driven metrics—such as the number of hours the vehicle drove without disengagement—the focus here is on behavioral aspects. Can the car anticipate a jaywalker in fog? Will it pause for an emergency vehicle when sirens aren't clearly heard? Can it navigate a detour without GPS? These are all part of the current assessment criteria. The goal is not perfection. It's resilience and common sense—traits human drivers use daily without thinking.
For AI developers, this changes the game. It encourages collaboration between hardware makers, cloud service providers, and behavioral scientists. Sensors alone won’t solve the problem. Neither will bigger models. What’s needed is a grounded, multi-disciplinary approach that deals with street-level unpredictability. The AI self-driving test hub reflects that shift. It’s not built around ideal conditions but around edge cases—the kinds of problems that keep engineers up at night.
Three secondary AI mobility centers are already being planned in southern Germany, each one focusing on different challenges: one will specialize in highway autonomy, another in urban delivery bots, and the third in long-haul trucking. All of them will plug into the main site’s data infrastructure. That kind of modular ecosystem could give Germany a head start in defining global norms around AI in transportation.
A new autonomous driving test hub in Germany takes a refreshing approach: it treats self-driving as an ongoing challenge, not a finished product. Rather than showcasing polished demos, it creates unpredictable conditions to reveal how AI handles real-world chaos. Weather, local habits, and language still confuse even advanced systems, and this hub exists to surface those flaws, not hide them. By expecting machines to fail and learn, engineers can focus on building better judgment into AI rather than chasing perfect scores. This mindset shifts the goal from polished promises to genuine progress, making autonomous vehicles something people might truly trust on the road someday.
Advertisement

Learn how process industries can catch up in AI using clear steps focused on data, skills, pilot projects, and smart integration

A former Pennsylvania coal plant is being redeveloped into an artificial intelligence data center, blending industrial heritage with modern technology to support advanced computing and machine learning models

How to use MongoDB with Pandas, NumPy, and PyArrow in Python to store, analyze, compute, and exchange data effectively. A practical guide to combining flexible storage with fast processing

Statistical Process Control (SPC) Charts help businesses monitor, manage, and improve process quality with real-time data insights. Learn their types, benefits, and practical applications across industries

Understand how logarithms and exponents in complexity analysis impact algorithm efficiency. Learn how they shape algorithm performance and what they mean for scalable code

Understand the Difference Between Non Relational Database and Relational Database through clear comparisons of structure, performance, and scalability. Find out which is better for your data needs

Uncover the best Top 6 LLMs for Coding that are transforming software development in 2025. Discover how these AI tools help developers write faster, cleaner, and smarter code

Few-Shot Prompting is a smart method in Language Model Prompting that guides AI using a handful of examples. Learn how this technique boosts performance and precision in AI tasks

Google AI open-sourced GPipe, a neural network training library for scalable machine learning and efficient model parallelism

What Hannover Messe 2025 has in store, from autonomous robots transforming manufacturing to generative AI driving innovation in industrial automation
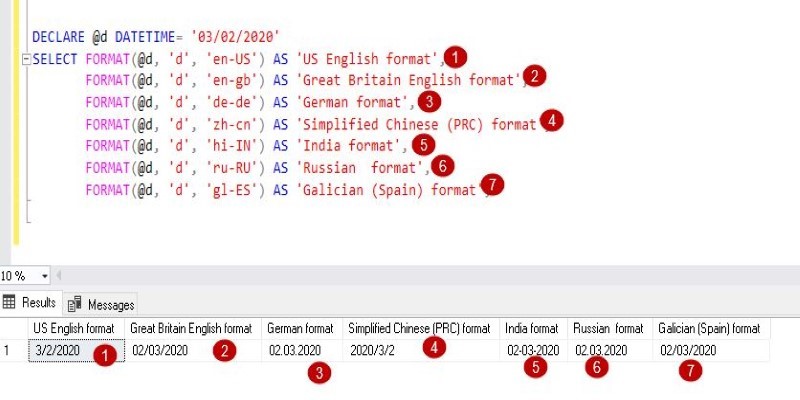
The FORMAT() function in SQL transforms how your data appears without changing its values. Learn how to use FORMAT() in SQL for clean, readable, and localized outputs in queries
How the SUMPRODUCT function in Excel can simplify your data calculations. This detailed guide explains its uses, structure, and practical benefits for smarter spreadsheet management